 |
|
| Option Calculators and Stock Screeners |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Chapter 3
|
| Volatility |
If the price of the underlying stock changes frequently, the option will cost more.
Volatility: The volatility is a measure of how likely it is that
the underlying stock price will change. This is typically computed by
taking the standard deviation of price changes over time. Different
option pricing models will use different time periods as a basis for
computing volatility. The price of both the call and the put increase
as the volatility increases.
The a stock's volatility changes frequently, it can change as result
of actual or anticipated changes in the underlying stock
price. Changes in volatility can occur over days and weeks or even
intra-day. Numerous option strategies trade on the basis of selling
options which are more expensive during periods of higher volatility
and buying options during periods of low volatility.
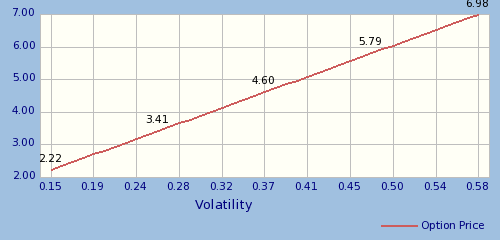 |
| Option price relative to change in volatility |
|---|
|
|
|
|
| Data Provided by HistoricalOptionData.com |
|
stock symbol for
straddle options strategy
leverage stock market
options butterfly spread
stock market symbol lookup
bull call spread
leverage stock trading
investment portfolio
options basics
volatility trading
dividend paying stocks
bear call spread
historical stock pricing
historical stock market data
stock trading strategies
best stock trading
stock ask price
butterfly diagonal
open interest vs volume
volume and open interest
|
| Optionistics is not a registered investment advisor or
broker-dealer. We do not make recommendations as to particular
securities or derivative instruments, and do not advocate the
purchase or sale of any security or investment by you or any
other individual. By continuing to use this site, you agree to
read and abide by the full disclaimer.
|
|


